
Electrical Wire and Electrical Cables
Electrical wire and electrical cable are a means of electrical connectivity between switches, outlets, appliances, and more. The installation and design of
electrical wires and cables are regulated by OSHA safety standards and the National Electric Code® (NEC®). Electrical wires and cables should be sized and
installed correctly to ensure safe operation.
Electrical Wire vs Electrical Cable
Electrical Wire

Electrical wire is an assembly of one or more conductors that are insulated but do not have an outer sheath/encasement.
The conductors in an electrical wire are either solid or stranded metal conductors.
Electrical wire insulation prevents electrical contact with other conductors, protects people from contact with
the electric current, and protects the conductor from environmental factors.
Shop All Electric Wire
Electrical Cable

An electric cable is an assembly of multiple insulated conductors bundled together within a protective outer sheath called a jacket that protects
the conductors from
dangerous elements such as dirt, fire, chemicals, and water. Electric cables are more versatile and can serve various
purposes like transmitting electrical power, data, or both.
Shop All Electric Cable
Wire Conductor Materials
Electric wiring conductors are usually made of aluminum or copper. Both aluminum wire and copper wire have their advantages — aluminum is cheaper but
becomes less conductive when oxidized. Copper wire has a higher cost but is more efficient over time. Both materials can be used in numerous settings and
applications with proper installation.
Copper Wire
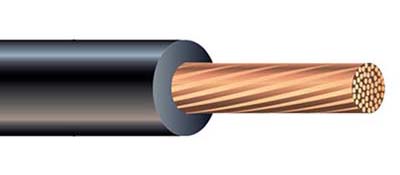
One conductor for electrical wires is copper, which is flexible and durable with an insulating jacket to protect against electrical fires or short-circuiting.
Copper wires have a high conductivity rate, meaning they work well with electronics. Copper wire is best used in power lines and low-voltage wiring
projects due to its low electrical resistance.
Shop Copper Wire
For copper wire prices, see the Elliott Electric Supply
Copper History Charts
for past and current pricing.
Aluminum Wire
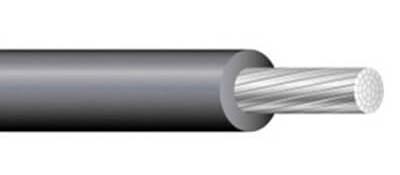
Another conductor for electrical wires is aluminum, which is more rigid than copper but provides a better ratio of conductivity to weight.
Additionally, aluminum wire is lighter, which reduces any wear on their support structures, and it has a lower corrosion resistance. While aluminum
wire has many uses, its most common is in power transmission and distribution.
Shop Aluminum Wire
Wire Size — Gauge
There are two sizing standards for wires depending on how small they are. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) standards are for common, everyday-use
electrical wiring seen in residential and commercial spaces whereas MCM (kcmil) measures the diameter
of large wires seen in public and industrial spaces.
AWG Wire Size
AWG wire is sized according to the American Wire Gauge which specifies the physical size of an electrical wire. The higher the gauge number the thinner the
wire, which means a 16 Gauge would be smaller
(thinner) than a 2 Gauge. Wire size limits how much electrical current can pass through the wire; the lower
the gauge number, the higher the amp capacity.
American Wire Gauge (AWG) Size Chart
| AWG Wire Size |
Wire Diameter |
Copper Wire Max Current* |
Aluminum Wire Max Current* |
| #16 |
0.0508 in |
24 amps |
- |
| #14 |
0.0641 in |
35 amps |
- |
| #12 |
0.0808 in |
40 amps |
35 amps |
| #10 |
0.1019 in |
55 amps |
45 amps |
| #8 |
0.1285 in |
80 amps |
60 amps |
| #6 |
0.1620 in |
105 amps |
85 amps |
| #4 |
0.2043 in |
140 amps |
115 amps |
| #3 |
0.2294 in |
165 amps |
130 amps |
| #2 |
0.2576 in |
190 amps |
150 amps |
| #1 |
0.2893 in |
220 amps |
175 amps |
| 1/0 |
0.3249 in |
260 amps |
205 amps |
| 2/0 |
0.3648 in |
300 amps |
235 amps |
| 3/0 |
0.4096 in |
350 amps |
270 amps |
| 4/0 |
0.4600 in |
405 amps |
315 amps |
* This sample maximum current capacity is given for a single insulated wire with 90°C insulation in free air with an ambient temperature of
30°C (86°F), NEC® table 310.17. The maximum current capacity for a wire is affected by the wire size, ambient temperature, the material
of the conductor, cable type, whether the cable is open to the air or within a cable or conduit, and the number of wires in the cable or conduit. For maximum current for
one to three wires in a cable, conduit or directly buried, see
Allowable Ampacities of Insulated Conductors.
For more than three conductors, see
Adjustment Factors for More Than 3 Current Carrying Conductors.
For maximum current at other ambient temperatures, see
Ambient Temperature Correction Factors Based on 30°C (86°F).
To calculate the current capacity for your wire, consult the NEC®, local electrical codes, and a professional electrician.
MCM (kcmil) Wire Size
MCM and kcmil are interchangeable terms measuring wire size in thousands of Circular Mils. A Circular Mil (cmil) is the area of a circle with a diameter
of a mil. A mil is a unit of length equal to 1/1000 of an inch.
MCM wire sizes have larger diameters than AWG wires. MCM (kcmil) wire size will affect how much current can pass through the wire;
the higher the wire size, the higher the amps capacity.
MCM (kcmil) Wire Size Chart
| MCM Wire Size |
Solid Wire Diameter |
Copper Wire Max Current* |
Aluminum Wire Max Current* |
| 250 kcmil |
0.500 in |
455 amps |
355 amps |
| 300 kcmil |
0.548 in |
500 amps |
395 amps |
| 400 kcmil |
0.632 in |
615 amps |
480 amps |
| 500 kcmil |
0.707 in |
700 amps |
545 amps |
| 600 kcmil |
0.775 in |
780 amps |
615 amps |
| 700 kcmil |
0.837 in |
850 amps |
670 amps |
| 750 kcmil |
0.866 in |
885 amps |
700 amps |
* This sample maximum current capacity is given for a single insulated wire with 90°C insulation in free air with an ambient temperature of
30°C (86°F), NEC® table 310.17. The maximum current capacity for a wire is affected by the wire size, ambient temperature, the material
of the conductor, cable type, whether the cable is open to the air or within a cable or conduit, and the number of wires in the cable or conduit. For maximum current for
one to three wires in a cable, conduit or directly buried, see
Allowable Ampacities of Insulated Conductors.
For more than three conductors, see
Adjustment Factors for More Than 3 Current Carrying Conductors.
For maximum current at other ambient temperatures, see
Ambient Temperature Correction Factors Based on 30°C (86°F).
To calculate the current capacity for your wire, consult the NEC®, local electrical codes, and a professional electrician.
Stranded Wire vs. Solid Wire
Solid wire and stranded wire are two common types of electrical conductors used in wiring and cabling. The main differences between solid and stranded
wire are their construction, flexibility, and applications. Choosing between solid or stranded wire depends on the specific application and
requirements of the wiring system.
Solid Wire
Solid wires are single-strand conductors like copper or aluminum. Although solid wire has a higher current capacity, it is more difficult to bend
and can even break if in constant motion.
Stranded Wire

Stranded wires are thin bundles of conductors twisted or braided together to create a more flexible wire. With increased flexibility, stranded wire is easier
to route in applications with bending and frequent movement.
Insulated Wire vs. Bare Copper Wire
Insulated Wire

In an insulated wire, the metal conductor is wrapped in a non-conductive insulating layer that is resistant to the electrical current flow and is corrosion-resistant.
Insulation colors are often used to distinguish the function of different electrical wires. The insulation material used will vary
based on the requirements for the installation.
Shop Insulated Wire
Bare Copper Wire

In contrast, bare copper wire is uninsulated, and therefore exposed. Bare copper wire is commonly used in electrical grounding, due to its high
heat resistance, flexibility and high conductivity, which maximizes the leakage current that the ground wire can handle. Overhead high voltage electrical transmission
and distribution also use bare copper wire.
Shop Bare Copper Wire
Types of Electrical Cable and Electrical Wire
Building and House Wire and Cable
Building and house wire and cable are used for retail and residential projects when constructing wiring systems for the properties. For residential and retail
projects, these may be called branch circuit wiring.
Electrical Wire Colors for Commercial and Residential Buildings
Whether thermoplastic or thermoset wires, these electrical wires will often be insulated so a
color-coded system can be used for installation and maintenance according to
NEMA guidelines.
Black
Wire
The standard color for hot (always live) wires used in outlets and switches
Red
Wire
The standard color for hot wires used in switch legs and smoke detectors
Yellow
Wire
Usually live wires pulled through a conduit used in switch legs or ceiling fans
Blue
Wire
Usually, live wires pulled through a conduit used in 3 or 4-way switches
White/Gray
Wire
Neutral wires, most often seen in white, that carries power back to a source
White Wire with
Black/Red Tape

A hot wire used similarly to a neutral white/gray wires
Green
Wire
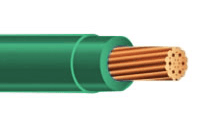
Grounding wire to ground a circuit; if a fault occurs, current is redirected into the Earth
Wire Naming Conventions for Residential and Commercial Building Electrical Wire
The NEC® standardized identification letters printed on electrical wires and electrical cables describe the protective capabilities of their
insulation.
Wire Name Label Meaning:
T
- Thermoplastic insulation
X
- XLPE thermoset insulation cross-linked with Polyethylene
H
- Heat resistant up to 167 ℉ or 75 ℃
HH
- High heat resistance up to 194 ℉ or 90 ℃
W
- Water-resistant wire used in wet conditions
N
- Nylon-coated to resist damage from oil or gasoline
FF
- Flexible fixture wire
-2
- Heat resistant in dry and wet locations up to 194 ℉ or 90 ℃
Common Types of Building Wire and Cable
Thermoplastic Insulated Wire
THHN Wire
THHN wire is a thermoplastic insulated, nylon-coated wire that can withstand high heat. Because THHN is inexpensive, it is often used
in residential or commercial construction. Most modern THHN wire has a dual rating THHN/THWN which is also suitable for wet conditions.
Shop THHN Wire
THWN Wire
THWN wire is a thermoplastic, nylon-coated wire that is rated for use in wet locations. THWN is heat resistant and can be used at temperatures up to
167 °F or 75 °C.
THWN can be used in conduit or exposed to the air. It can be used for residential and commercial buildings or outdoor applications.
Shop THWN Wire
THWN-2 Wire
THWN-2 wire is an improved wire with thicker insulation that is both high heat and water resistant. It can be used for indoor and outdoor locations and withstand
dry and wet temperatures up to 194 ℉ or 90 ℃. THWN-2 is a dual-rated wire approved for both THWN and THHN applications.
Shop THWN-2 Wire
TFN Wire
TFN is a thermoplastic, nylon-coated fixture wire with high heat resistance for electrical fixtures. TFN has a solid conductor wire which limits its
flexibility compared to TFFN wire. TFN is available in smaller wire sizes like 16 AWG and 18 AWG.
Shop TFN Wire
TFFN Wire
TFFN is a fixture wire with a stranded copper conductor that adds additional flexibility, making it more adaptable to various electric
fixtures. TFFN is also high-heat resistant and only available in 16 AWG and 18 AWG sizes.
Shop TFFN Wire
Thermoset Insulated Wire
XHHW-2 Wire
XHHW-2 wire has thermoset insulation with XLPE (cross-link polyethylene) instead of thermoplastic, which makes it stronger and more flexible than THWN-2. XHHW-2 may
be priced higher, but it's less susceptible to damage and will last longer.
Shop XHHW-2 Wire
Romex™ Wire or NM Cable (Types NM, NMC, NMS)

Although all Non-Metallic Sheathed Electrical Cable is commonly called Romex™, Romex™ is the trademarked name for Thermoplastic-Sheathed Cable (TPS), most
specifically Romex™ NM-B sheathed electrical cable manufactured by Southwire. Romex™ equivalent NM cables contain multiple THHN wires under one PVC sheath. They are used in residential indoor areas, typically used for
lighting applications and appliances.
Shop All Nonmetallic-Sheathed Cable
Cable Color Coding System for Romex™ Equivalents
Romex™ equivalent NM cables have an insulated jacket that comes in a variety of colors that represent the size or use of electrical wires housed within the cable.
As this coding system is not standardized but rather something most manufacturers choose to
follow, all cable jackets have labeling on the outside to indicate how many wires and what kind of wires are inside the sheathing. Additionally, often the
wires within the cable jacket have their own color-coded system to indicate neutral (white) and hot (black or red) wires.
Most manufacturers follow these guidelines:
White Romex™ Type Cable
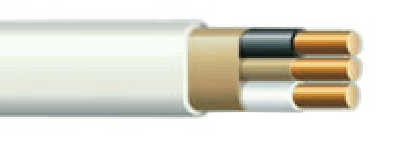
14 Gauge Wires
General applications needing 15‑20 amp circuits
Yellow Romex™ Type Cable
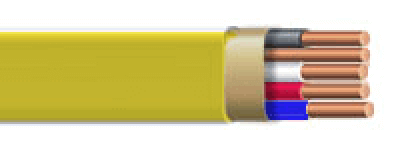
12 Gauge Wires
General applications needing 20 amp circuits
Orange Romex™ Type Cable
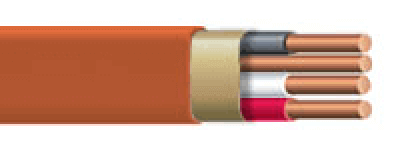
10 Gauge Wire
30 amp loads like ACs or water heater feeds
Black Romex™ Type Cable
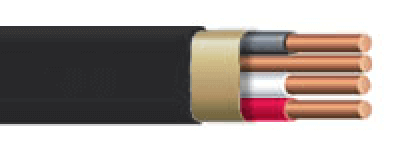
6 Gauge Wire or 8 Gauge Wire
General applications needing 40‑50 amp circuits
Gray Romex™ Type Cable

Does not designate a wire size
Water-resistant wires meant for underground applications

Machine tool wire, also known as MTW wire, is a type of electrical wire that is specifically designed for use in machine tools and other industrial equipment.
It is often used in environments where the wire needs to withstand mechanical stress, oil, and other factors commonly found in manufacturing settings
such as control cabinets, machine tools, and appliances.
Shop All Machine Tool Wire
PV Wire (Solar Photovoltaic)
Solar photovoltaic (PV) wire is a single conductor wire that connects the different components of solar panels (PV systems).
PV wire works well for these jobs as they can operate under intense heat, sunlight, and weather conditions. PV wire
has thick XLPE insulation for above-ground or direct burial installation.
Feeder Cable and Underground Cable — Direct Burial Wire
Underground Cables
Underground cables and wires are made to safely be installed and remain underground without the need for a conduit or additional protective covering.
Typically, they have a conductor, insulating system, and sheath/jacket dependent on the environment in which they're used to provide resistance to moisture,
sunlight, and soil chemicals.
The three most common methods are:
Conduits and Ducts
Most common in urban areas and commercial buildings for organized cable management and protection.
Manholes and Handholes
Allows access to underground utility networks for maintenance and repairs in various urban settings.
Trenches and Direct Burial
Suitable for areas requiring minimal excavation such as large-scale utility installations or residential settings.
Shop All Underground Cables
Direct Burial Wire

Direct Burial Wire is a special wire designed to be buried underground. A thermoplastic sheath keeps out moisture and protects the internal
wiring components. Direct burial wire uses include underground power grids, post lights, sprinkler systems, and more.
Shop All Direct Burial Wire
UF-B Wire — Underground Feeder (UF) and Branch Circuit (B) Cable

A UF-B Cable is an underground feeder and branch circuit cable. UF-B has an outer covering of non-metallic material, making it usable as
direct burial cable in wet, dry, or corrosive locations and also suitable for use in cable trays.
Shop UF-B Wire
URD Cable — Underground Residential Distribution

A URD cable is an underground residential electrical distribution cable. Although not permitted for indoor use, URD cables work well
for electrical panels, home feeders, and direct burial depending on their current ratings.
Shop URD Cable
MHF Cable — Mobile Home Feeder Cable

MHF cable, or a mobile home feeder cable, is a specialty cable with an aluminum conductor and insulation made of XLPE
(thermoplastic polymer with modifications). MHF cables can be direct burial, home feeders, or electrical panels depending on their current capacity.
Shop MHF Cable
Underground Tracer Wire
Tracer wire is typically a coated copper wire that is resistant to chemicals, moisture, abrasions, pressure, and oil. A tracer wire is similar
to a THHN wire except it lasts longer and provides more protection. Since they are meant for direct burial, tracer wires
also have a signal for easy location.
Service Entrance Cable and Service Drop Cable (Type SE Cable)

A service entrance cable or service drop cable is an electrical cable bundle that runs from a building to an electric power pole.
These are typically made with lightweight aluminum to be more cost‑effective.
Shop SE Cable
Flexible and Portable Wires, Cables, and Cords
Flexible and portable wires, also known as portable cords or flexible cords, are electrical cables designed for applications that require mobility,
flexibility, and resistance to bending, twisting, and stretching. These wires are constructed with stranded conductors to enhance flexibility, and they
are typically encased in durable yet pliable insulation materials, such as rubber or thermoplastic.
Lamp Cord
SPT-1 vs SPT-2 Wire
SPT is an acronym for Stranded Parallel Thermoplastic Wire. The thickness of the insulating jacket is one difference between SPT-1 wires
and SPT-2 wires; SPT 1 insulation is 0.03" thick whereas SPT 2 insulation is 0.045" thick. Another difference is that SPT-1 wires are typically
cheaper and more common, but with the additional insulation, SPT-2 wires offer higher levels of electricity and are better protected.
While these work for many lamp types, they're most commonly used in string lights.
Shop SPT Wire

SO Cable
Flexible and portable wires, cables, and cords have a standardized naming system that indicates the intended use for each wire/cable. These are referred to as
SO cables, as each type has these two letters.
SO Cable Name Label Meaning:
O
- Oil-Resistance Insulation
W
- Water and Moisture Resistant
E
- Thermoplastic Elastomer
OO
- Oil-Resistance Insulation and Jacket
SOOW Cable
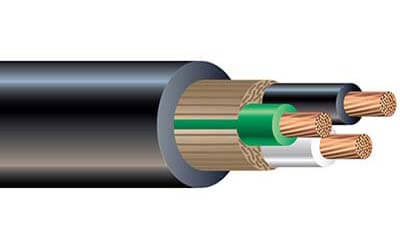
Featuring a heavy-duty thermoset elastomer jacket, SOOW cable is one of the most popular portable options used in industrial equipment,
welding and motor leads, mining applications, heavy tools, and more because of its strong resistance to water, oil, sunlight,
and extreme temperatures.
Shop SOOW Wire
SEOOW Cable
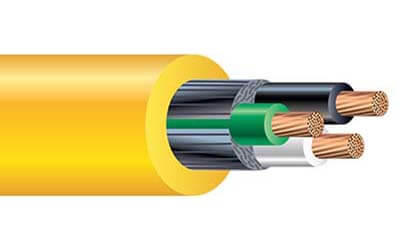
SEOOW cable is a more flexible cable designed with an additional protective jacket, typically made from a thermoset elastomer, that provides excellent
resistance to water, oil, sunlight, and extreme temperatures.
Shop SEOOW Cable
SJOOW Cable
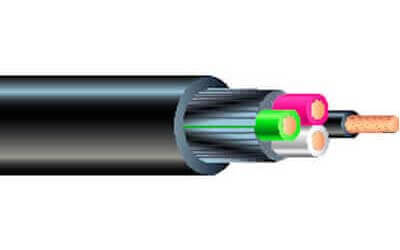
SJOOW cables are widely used in heavy-duty jobs due to their durability, water resistance, and temperature tolerance. Their sturdy
outer jacket makes them suitable for a wide range of applications including power tools, portable machinery, and equipment that
require dependable power connections in varying environments.
Shop SJOOW Cable
SJEOOW Cable
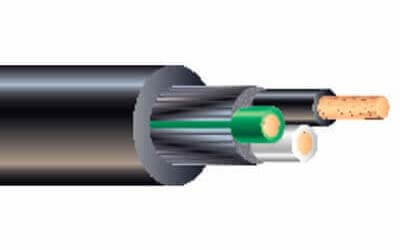
SJEOOW cable is a highly flexible electrical cable with a tough and weather-resistant jacket that can withstand exposure to oil,
water, sunlight, and extreme temperatures. This makes it an ideal option for appliances and equipment, or even outdoor and underwater locations.
Shop SJEOOW Cable
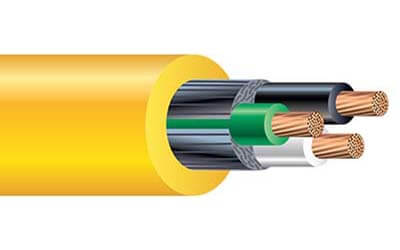
SJTOW Cable
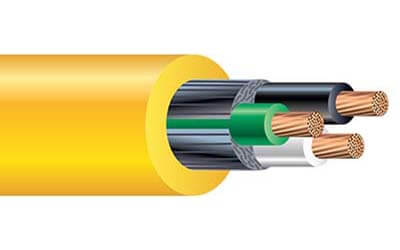
SJTOW cable has a durable jacket that provides resistance to sunlight, water, and extreme temperatures, making it suitable for
various applications including power tools, portable appliances, motors, washing machines, portable lights, floor-maintenance equipment,
and more with a flexible design.
Shop SJTOW Cable
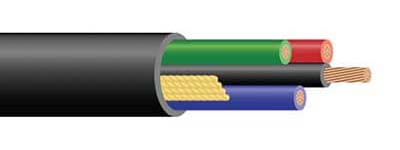
STOOW Cable
Designed with a combination of oil-resistant, water-resistant, and weather-resistant properties, STOOW cable is often used in industrial settings,
outdoor applications, and temporary power distribution such as lighting extensions, consumer
applications, and portable power. However, STOOW cable is a less flexible cable due to the thermoplastic (T).
Shop STOOW Cable
Industrial Cable and Wire
Industrial cable refers to a broad category of electrical cables engineered for toughness, durability, and versatility, making them suitable for a
wide range of industrial applications, including manufacturing, automation, machinery, and control systems. Industrial cables come in various types
designed to transmit electrical power, signals, or data while withstanding exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures,
moisture, mechanical stress, and electromagnetic interference, which makes them a critical component of modern industrial infrastructure.
Cable Tray Wire (Tray Cable)
A cable tray wire, often referred to as a tray cable, is two or more insulated conductors within a nonmetallic sheath used specifically in raceways,
cable trays,
or other support systems. Additionally, they can come in different colored jackets to indicate specific purposes whether for control, lighting, or signal.
Shop All Tray Cable
Types of Tray Cables:
THHN-PVC

THHN-PVC wire has a durable and heat-resistant PVC jacket for direct burial and does not require a conduit.
Shop THHN-PVC Cable
XLP-PVC

XLP-PVC wire has a type of polyethylene insulation (commonly called Teflon) and a PVC jacket for
corrosion resistance and extended use.
Shop XLP-PVC Cable
EPR/CPE

EPR/CPE wire has a CPR flame-retardant sheath and EPR insulation, but they are also resistant to chemicals,
sunlight, weather, and abrasions.
Shop EPR/CPR Cable
For more information about raceways and cable trays, see our
Raceway, Conduit, and Cable Tray page.
Armored Cable and Metal Clad Cable
AC (Armored Cable also called BX), MC (Metal Clad), SWA (Steel Wire Armored), AWA (Aluminum Wire Armored), and STA (Steel Tape Armored) cables are types of electrical cables
used for wiring in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
These cables provide a layer of physical protection for the enclosed conductors, reducing the risk of damage due to mechanical stress, impact, or abrasion.
This is especially crucial in areas where cables may be exposed to physical hazards. For these reasons, many electrical codes and standards require the use
of these cables in specific applications to ensure compliance with safety and performance requirements.
What is Armored Cable?
Armored cable, often referred to as AC cable or BX cable, is a type of electrical wiring that features a metal sheath for physical protection. What makes
AC cable unique is that it doesn't have a grounding wire and instead, uses the metal sheath as its grounding component. Armored cable is commonly used
in a variety of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial wiring, where additional protection is needed.
Shop Armored Cable
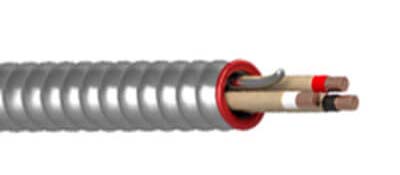
When to Use Armored Cable?
Armored Cable (AC Cable) should be used in indoor electrical installations where the wiring will need additional physical protection and grounding capabilities.
AC cable is often used as
residential wiring for branch circuits and feeder wiring. In commercial and industrial locations, AC cable is used in various applications where wiring
needs protection against mechanical stress, impact, or environmental factors. Armored cable
Metal clad cable is used in situations where enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), physical damage, or moisture is needed.
MC cable can transfer higher power rates at greater distances. With a PVC jacket, metal clad cable can be used in harsh outdoor environments
and be used as an underground cable.
Shop Metal-Clad Cable

Although armored cable and metal-clad cable both have a metal-based sheath, there are several differences in their design, wires, and function. AC cable uses its
outer sheath as part of the ground, but MC Cable does not use the sheath as part of its grounding and instead uses a ground wire. AC cable is for indoor use only because it
doesn't have a PVC thermoplastic jacket. MC cable has a PVC water-resistant jacket, making it appropriate for indoor or outdoor and underground locations.
AC/BX Cable
- No grounding wire - its metal jacket is the grounding component
- Used indoors only
- No PVC jacket
- Not rated for direct burial
MC Cable
- Grounding wire
- Used indoors and outdoors
- Has PVC jacket
- Rated for direct burial
Steel Wire Armored (SWA) Cable and Aluminum Wire Armored (AWA) Cable

Steel Wire Armored Cable (SWA) features a layer of galvanized steel wires that serve as protective armor, while Aluminum
Wire Armored Cable (AWA) features a layer of aluminum wires serving as protective armor. A typical SWA or AWA cable has an inner conductor wrapped
in XLPE insulation, a protective bedding layer, an armor layer and an outer sheath.
This armored construction shields the cable from physical damage, such as crushing, impact, and abrasion, making it ideal for use in industrial
settings, underground installations, and areas with potential hazards. Some SWA and AWA cables also have UV protection in their outer sheath.
SWA cables can cause overheating when the electromagnetic field generated by the current flowing in the conductor induces eddy currents in the steel armor.
Because aluminum wire is non-magnetic and thus does not have eddy currents caused by the electromagnetic field, AWA cables are
often used with single-core cables to eliminate the overheating issue seen in SWA cables.
Shop SWA Cable
Steel Tape Armored (STA) Cable
Steel tape armored cable, also known as STA cable, features a layer of steel tape wound around the insulated conductors. The steel tape serves as a
protective armor, providing mechanical protection against crushing, bending, and impact. STA cable is commonly used in industrial and
heavy-duty applications where robust mechanical protection is required such as underground installations.
Marine and Drilling Cable

Marine cable, also known as shipboard cable or marine-grade cable, is a type of electrical cable specifically designed and constructed for
use in maritime environments and applications. These cables are engineered to withstand the unique challenges posed by marine conditions, such
as exposure to moisture, saltwater, vibration, and mechanical stress.
Drilling cable, also known as drill cable or oilfield cable, is constructed to withstand harsh environmental factors such as extreme
temperatures, mechanical stress, and oil and chemical exposure. Drilling cables serve as vital components in drilling equipment,
providing power, control, and data transmission to various machinery and sensors used in drilling rigs and oilfield applications.
Shop Marine and Drilling Cable
Low Voltage Wire — Structured Cable
Low-voltage wiring, also called structured wiring, is used to connect doorbells, TVs, thermostats, and data communication networks connecting computers, routers, phones, and
printers. Because low-voltage wire has more energy lost per foot of cable compared to high-voltage cable, low-voltage cable typically has a limited range of 100-150 feet.
Low-voltage, structured cable and wire carry 50 amps or less current.
What are the Advantages of Low-Voltage, Structured Cabling?
- Low-voltage, structured cable is less likely to cause interference in nearby cables and equipment than standard high-voltage cable.
- Because low-voltage, structured cable carries less current, low-voltage cable has a lower risk of electrical shock injuries than high-voltage cable.
- Low-voltage, structured cable requires less energy to operate, reducing power costs.
- Low-voltage, structured cable is a smaller, flexible cable that can be easily routed through walls and ceilings.
Thermostat Wire and Cable
Thermostat wire is a type of copper wire encased in color-coded insulation. A thermostat cable contains color-coded wires encased in an
outer sheath covering jacket. The thermostat wire connects to a control board that controls either a thermostat or another low-voltage electrical device.
Shop Thermostat Wire
Thermostat Wiring Color Code
The following thermostat wiring color code describes how to connect thermostat wire colors to the correct corresponding terminal of your thermostat.
For further details for connecting your specific thermostat, see your manufacturer's thermostat instructions since thermostat wire colors and terminal labels may vary.

Thermostat Yellow Wire
Y Terminal
Connects the thermostat to the AC cooling unit.
Thermostat Green Wire
G Terminal
Connects the thermostat to the fan.
Thermostat White Wire
W Terminal
Connects to the furnace or heating source.
Thermostat Red Wire
R, Rc or Rh Terminals
Connects the thermostat to the power source for AC and Heat.
Thermostat Brown Wire
E Terminal or C Terminal
Connects the thermostat to the emergency heat source or Common.
Thermostat Orange Wire
O/B Terminal
Connects the thermostat to the heat pump.
Thermostat Blue Wire
C Terminal
Common "neutral" or c-wire; Provides constant power for programmable thermostats. The C‑wire may also be black, brown, or purple.
Thermostat Black Wire
C Terminal
Common "neutral" or c-wire; Provides constant power for programmable thermostats. The C‑wire may also be blue, brown, or purple.
Thermostat Purple Wire
C Terminal
Common "neutral" or c-wire; Provides constant power for programmable thermostats. The C‑wire may also be blue, brown, or black.
Thermocouple Wire and Cable
A thermocouple wire is used to make a sensing point (or probe) that can measure temperature. These consist of two different metals to provide
a millivolt value that is measured by the sensor. Thermocouple wires are commonly color-coded with a red negative lead sheathed in a brown jacket.
Shop Thermocouple Wire

Thermocouple wires and cables typically come encased in one of the following:
PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly used as insulation due to it being flexible, durable, and affordable.
FEP
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP) is transparent, chemical resistant, and has high thermal stability.
PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is durable to high heat, weather corrosion, and resistant to UV radiation.
PFA
Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) shares the same properties as PTFE but is melt-processable, which makes it more flexible.
Network Data Cable
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet cables, such as Cat 5e cable and Cat 6 cable, serve as the foundation of wired local area networks (LANs) by facilitating the exchange of data
packets between connected devices, which enables high-speed, reliable communication between network devices like as computers, servers,
switches, and routers. Data transfer speeds depend on the specific category of modern Ethernet cable and range between 1 Gbps and 40 Gbps.
Shop Ethernet Cable

Cat5e vs Cat6 Ethernet Cable
CAT5e (Category 5e) and CAT6 (Category 6) cables are both types of twisted-pair Ethernet cables used for networking purposes,
but they have differences in terms of performance, maximum data speeds, and other characteristics. Here are the key differences
between CAT5e and CAT6 cables:
Cat5e Cable
Cat 5e cable can support applications up to 100 Mbps and provides ELFEXT (Equal Level Far-End Crosstalk) and Return Loss Performance.
- 1000 Mbps or 1 Gbps data transfer speeds within
328 feet (100 meters)
- 100 MHz bandwidth capacity
- 24 AWG conductors
- Backward compatible with CAT5 and CAT3
- Less expensive than CAT6
Shop CAT5e Cable
Cat6 Cable
In contrast, Cat 6 cable supports frequencies up to 1000 Mbps and is regularly used for Ethernet cables.
- 10 Gbps data transfer speeds within 121 feet (37 meters). Supports 1 Gbps over the standard 100 meters
- 250 MHz bandwidth capacity
- 23 AWG conductors
- Better backward compatibility with CAT5e components
- Priced higher for higher performance specifications
Shop CAT 6 Cable
For more information on The Category Rating System, see our
Ethernet Cable Guide page.
Coax Cable

Coaxial cable is a type of electrical cable that consists of a central conductor, an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer
insulating layer meant to block signal interference. It is commonly used for transmitting electrical signals, particularly for
television signals, internet connections, and other data transmission applications.
Shop Coax Cable
HDMI Cable
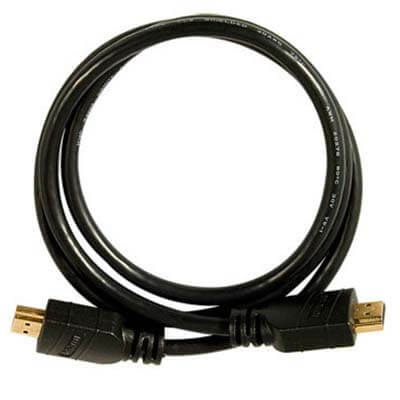

An HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) cable is a digital cable commonly used to transmit high-definition audio and video between electronic devices
including computer monitors, gaming consoles, and TVs. There are three kinds of HDMI cables with varying bandwidth, resolution quality and refresh rates:
Standard HDMI
Max Bandwidth: 2.25 Gbps
High-Speed HDMI
Max Bandwidth: 10.2 Gbps
Ultra-High-Speed HDMI
Max Bandwidth: 48 Gbps
Shop HDMI Cables
Wire Connectors

Wire connectors are devices used to join or terminate electrical conductors, providing secure and insulated connections.
Shop All Wire Connectors
Quick Disconnect Wire Connectors

Quick disconnect wire connectors have terminals that slide together and allow wires to connect or disconnect without the need for tools.
Shop Quick Disconnect Connectors
Bushing Connector

Bushings provide a protective insulated passageway for electric cable, typically using porcelain, paper, or resin insulation
Shop Bushing Connectors
MC Connectors

MC connectors, short for metal-clad connectors, are fittings used in electrical installations to secure and connect metal-clad (MC) cables.
Shop MC Cable Connectors
Cable Puller

Electric cable pullers operate by using a motorized mechanism to grip and pull electrical cables through conduits or other pathways.
Shop Cable Pullers
Cable Cord Grips
Cable cord grips, also known as cable glands or strain reliefs, secure and seal the connection points of electrical cables and equipment panels.
Shop Cord Grips
Push-In Wire Connectors

Push-on wire connectors are a time-saving device that connects stripped wires by clamping them in place, rather than twisting them together.
Shop Push-In Wire Connectors
Cable Cutter

A cable cutter is a hand tool or power tool designed specifically for cleanly cutting through electrical cables, including AC and MC cables.
Shop Cable Cutters
Pull Tape

Pull tape, also called pulling tape or fish tape, is a strip of material that helps pull or fish cables through conduits and tightly enclosed spaces.
Shop Pull Line Tape
Cable Clamp
Connector

Cable clamp connectors secure non-metallic cables and flexible cords to metal enclosures like outlet boxs for a safer and stronger connection.
Shop Clamp Connectors
Electric Meters &
Testers

Electric meters and testers are diagnostic tools used to test the various properties of an electrical current within a live wire or cable.
Shop Meters and Testers
With locations across multiple states, Elliott Electric Supply
understands the electrical industry and your needs, unlike big-box retailers and e‑commerce corporations. Now, you can access our supplies
and services more conveniently using our mobile‑friendly website and through our updated
customer app.
From copper wire to armored cable, we've got your electrical needs covered. With great pricing, extensive inventory, and fast delivery,
you'll find no better wholesale electrical supplies distributor online than Elliott Electric Supply.
Check Out Our Other EES Products:
WARNING: For safety, call a licensed electrician and consult the NEC®. All licensed electricians have passed examinations covering
the National Electric Code®, know state and local building codes, and may carry insurance to cover damages.